EC meters are a very important piece of hydroponic equipment that many people don’t use. Especially if you are a beginner you may not have even heard of using an EC meter in hydroponics. But let me tell you that it can make or break your whole hydroponic system.
Basically, an Electrical Conductivity meter or EC meter is an electrical device that measures the number of free-floating ions (N+ or OH–) or the number of salts in the nutrient solution represented as the concentration of a nutrient solution. The EC meter gives the measurement in millisiemens per centimetre (mS/cm) which can be converted into PPM.
In this article, I am going to tell you the best EC meters available for hydroponics in the market. Along with that, I am also going to cover all the essential points that you must know before buying or using an EC meter.
This article is the ultimate guide to buying an EC meter for hydroponics.
Let’s get started with our top 5 EC meters for hydroponics and then we will answer all your questions regarding the usage, calibration and ideal EC value for hydroponic vegetables.
Disclosure: Some of the links below are affiliate links, meaning at no extra cost to you, I will earn a commission if you click through and make a purchase.
Top 5 EC meters for Hydroponics
1. Bluelab PENCON Pocket Tester
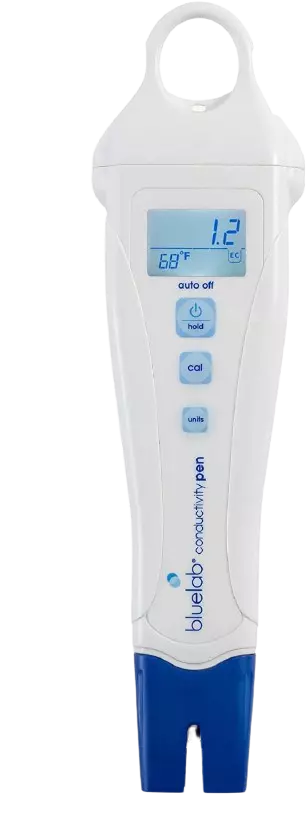
Bluelab has become a well-known brand when it comes to pH and EC meters. They provide good quality, durable, and easy to use hydroponics equipment.
The Bluelab PENCON is a very handy EC meter that also measures temperature in both degrees Celsius and Fahrenheit. This meter can provide you with reading in various formats like EC, CF, PPM 500 and PPM 700. I have given the formula to convert EC into PPM in the later sections of this article.
This EC meter has a range of 0 to 10.0 EC and can resolve up to 0.1 EC i.e you can get results in the difference of 0.1 EC. The body of this EC pen is built to last long and is waterproof. It also uses a smart technology that makes the probe adjust the readings for surrounding temperature.
The temperature readings are accurate in the range of 1-degree Celsius and 2 degrees Fahrenheit.
Additionally, the Bluelab PENCON is pre-calibrated from the factory and ready to use. It gives an LCD output where both EC and temperature readings are displayed. In the package, you also get a AAA battery so that it’s ready to use out of the box.
There is a 1-year limited warranty with this product valid only with proof of purchase. Make sure you save that invoice to get the warranty benefits.
2. Apera Instruments, LLC-AI314 Premium EC60

Apera LLC-AI 314 premium EC pen is one of a kind handy hydroponic equipment for the gardener on the go. It uses a platinum sensor probe to determine accurate results every time you use it.
The LCD display given on the top of the device gives EC and temperature readings. It uses colour coding for the display lights. Blue for measurement and green for calibration. You can check EC readings, TDS, salinity, and temperature on that display. The IPV 67 ratings protect it from being damaged from water splash.
The range of EC meters is 0 to 20 mS/cm. The auto temperature calibration takes into account the surrounding temperature to adjust EC accordingly. It can measure temperature up to 50 degrees Celsius.
This device comes packed in a safe plastic kit which consists of a pre-mixed conductivity solution with an EC of 1413 uS/cm and another one with an EC of 12.88 mS/cm. You also get some calibration bottles, storage solutions, AAA batteries, a lanyard, and a quick instructions guide inside the carrying case.
All in all, the Apera EC meter kit is an excellent choice for beginners who are wanting to increase their technical expertise in the field of hydroponics and get the maximum yield out of their harvest.
Also, Read “The Only pH Down guide you’ll ever need for Hydroponics“
3. VIVOSUN TDS Tester 3-in-1

VIVOSUN TDS and EC tester are one of the cheapest hydroponic testing equipment available in the market. This is something that anyone can buy even if you are not into hydroponics but need to measure EC or TDS of your drinking or irrigation water then you can use this.
Coming to the specifications, this meter gives three outputs on a digital display mainly TDS, EC, and temperature. You cannot measure pH levels with this probe.
The range in which this device can measure the TDS is 0-9990 PPM and EC in the range of 0-9990 uS/cm or 0-9.9 mS/cm. The device is factory calibrated but may need calibration at your home before using it to detect EC of any hydroponic nutrient solution.
It is a low cost and easy to use, portable EC meter for beginners. Although this device is used mainly for testing the EC and TDS of plain waiter or normal solutions. I have put this on this list because I think it can work well for hydroponic solutions as well.
Note: This device may not be the most accurate of them all, but for a beginner or someone with an indoor hydroponic setup, this is an amazingly low-cost meter and great for learning purposes.
4. Bluelab MONGUA Guardian Monitor
The Bluelab MONGUA is hands-down the best EC meter you can have for your hydroponic system. It is made for a more professional hydroponic setup. In addition to EC, it also reads temperature and pH levels in real-time.
So, if you are a beginner then this one may not be well suited for you.
This hydroponic equipment is majorly for those who want to monitor their nutrient solution, reservoir, or controlled greenhouse environment 24×7. As the device comes with a wall mounting setup, you can easily install it anywhere near your hydroponic system and track live data.
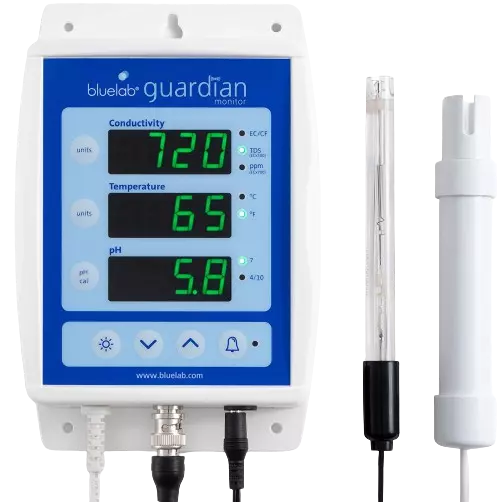

The Bluelab MONGUA provides accurate EC readings in EC, CF, PPM 500, and PPM 700 units. The temperature is measured in C/F and the pH value is measured on the standard pH scale.
One distinguishing feature of this EC meter is that it has an LCD green display. The green light from the display is beneficial for the hydroponic plants too. This is important because this device is used for 24×7 tracking. Also, there are simple push buttons on the panel to change the units.
It comes in a package with a calibration buffer solution, international power supply, and a 2-year limited warranty.
Also, Read “21 Best Hydroponic Gardening Gifts ever“
5. Hanna Instruments HI 9813-6N
This one is similar to the Bluelab MONGUA. Again I will say that this is for those who either already have or want to build a large hydroponic system or greenhouse that needs constant monitoring.

Let’s get straight to the point. It does measure EC, pH and temperature with unit options like EC, CF, and PPM 700, C and F. You can easily change the reading by the press of a button.
Note: There is no support for the PPM 500 scale.
The Hanna HI-9813 6N has an EC reading resolution of 0.01 mS/cm. The range for EC is 0 – 4.0 mS/cm with an error of +-2%. For pH, it has a range of 0 to 14 and a minimum resolution of 0.1 pH. It can also measure temperature up to 60 degrees celsius.
Unlike the Bluelab MONGUA, the Hanna HI 9813-6N doesn’t have a wall-mount and comes with a battery which makes it portable and highly accurate. The package comes with a buffer solution for EC calibration and one for pH calibration and one more for calibrating the TDS meter.
Additionally, they also provide a cleaning solution for the probe which makes it last longer. You can also replace the probe for some extra cost if it gets clogged or broken.
All in all, if you are looking for highly accurate, sturdy, and reliable hydroponic equipment that can measure pH, EC, and temperature, then Hanna HI 9813-6N is a great investment.
6. AERO-GRO 5 in 1 TDS/pH Meter
The AERO-GRO 5-in-1 TDS/pH Meter is a versatile and compact device designed for measuring the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) and pH levels in various aqueous solutions.
It is commonly used in hydroponics, aquaponics, water treatment, and general gardening applications. This multi-functional meter offers a convenient and efficient way to monitor water quality, ensuring optimal conditions for plants and aquatic life.
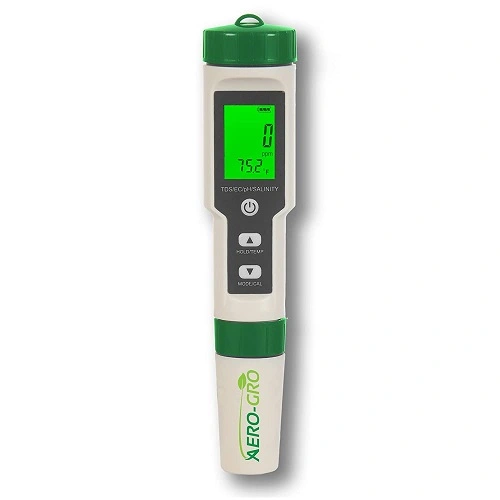

The key features of the AERO-GRO 5-in-1 TDS/pH Meter include:
- TDS Measurement:
- pH Measurement
- Accuracy and Calibration
- User-Friendly Design
EC Meter Basics
Why use an EC meter in hydroponics?
If you are new to hydroponics, you must be wondering why do you even need to use an EC meter? Well, in the beginning when I started I was of the same opinion. So, let me tell you exactly why you need an EC meter in hydroponics.
By now you know that an EC meter measures the concentration of the nutrient elements in the hydroponic solution. So, this plays a very important role in maintaining your hydroponic system.
When we start a system, the hydroponic solution we use is the recommended range of pH level and PPM. This is because we follow the steps given by the manufacturer to make a gallon or 5 gallons of nutrient solution.
But as the plant grows it utilizes some nutrients more than others, the hydroponic nutrient solution starts to get absorbed and also temperature comes into effect. This modifies the concentration level of the hydroponic solution and if not corrected the plant may lead to either wilting or bolting and eventually die.
Also, if the water you are using to make the hydroponic nutrient solution has more than 75 ppm concentration of bicarbonates this will make the solution more alkaline which will result in a higher pH level of the nutrient solution. For this reason, you have to use an EC meter to check the PPM levels of your water and the solution.
To reduce the pH level of your hydroponic nutrient solution you can use acidic fertilizers like phosphoric acid, citric acid, or vinegar.
In conclusion, it is very important to keep checking the EC of the hydroponic solution in regular intervals and correct the concentration whenever it skews. This process is also called nutrient management and an EC meter is key equipment used in the process.
I am sure, now you know why an EC meter is important in hydroponics.
How to use an EC meter in hydroponics?
An EC meter is used for nutrient solution management in hydroponics. It has a similar kind of application in aquaponics and freshwater systems also. So, how do you use that equipment?
Now, you know how to calibrate the EC meter. So, once you have calibrated it you can go on with the following steps. I am considering that you are building a new hydroponic system so that this will be more meaningful for my audience who are new to hydroponics.
Note- I am assuming that you have already calibrated your EC meter. If not, read the next section first.
Step 1 – Fill the reservoir or tank or a tub with either filtered water or tap water. Be sure to check the pH and EC of the water before using it in the hydroponic system.
Step 2 – Now add the hydroponic fertilizer to the water. Use the instructions given by the nutrient manufacturer for the quantity to be added.
Step 3 – Stir the solution until it mixes well. After that put the measuring head of the EC meter into the solution. The readings may fluctuate initially. Wait for it to become stable.
Step 4 – If the reading is higher than the optimum level required for the hydroponic plant you are growing, then you have to dilute the solution by adding more water and repeat Step 3.
I have given an EC Reading chart for the optimum level of EC and pH values according to the vegetables below in this article. It is also available to download. Do check it out.
Step 5 – If the reading is lower than the optimum level then add more nutrient fertilizer to the solution and repeat step 3.
Step 6 – Rinse the probe and store it in the cleaning fluid.
How to calibrate an EC meter?
Now once you have bought an EC meter, you should know how to use it and the first step in measuring the EC of any kind of solution is to first calibrate your EC meter.
EC meter calibration is an important step in determining the EC of any solution and it cannot be skipped because you need to have a reference point so that you know your EC meter is working just fine.
To calibrate the EC meter you need something called a Buffer solution. A buffer solution is an ideal solution whose EC is known to you already. You can buy any standard conductivity buffer solution on Amazon easily. The buffer solution generally has an EC value of 1.41 mS/cm.
So, before using the EC meter on the nutrient solution you need to measure the EC of the buffer solution. If the EC meter shows the correct reading as prescribed on the buffer solution bottle, then you are good to go. Otherwise, you will have to check for more solutions.
In general, 2-point conductivity buffer solutions are used for calibration which gives better accuracy. 2-point meaning using two buffer solutions for calibration instead of just one.
I hope, now you know how to calibrate an EC meter for your hydroponic system.
Also Read “Ideal Temperature and Humidity for Grow Tent“
EC to PPM/TDS Conversion
In case you are wondering how to convert EC units into PPM units then let me walk you through it. The Electric Conductivity meter measures in mS/cm or dS/m but manufacturers use PPM to demonstrate the concentration of a nutrient solution. Also, different countries use different PPM scales, in the USA they use a 500 scale or a 650 scale and in the UK a 700 scale is used.
So this is how you convert EC to PPM
In USA
PPM500 = EC x 500 or,
PPM650 = EC x 650
In UK
PPM700 = EC x 700
1 mS = 10 CF = 700ppm
EC, pH, and PPM Reading chart for Hydroponics
This is the most demanded resource in the hydroponic community. I have searched for over 50 documents to get this data. The table below gives the pH, EC, and PPM requirements for 80 vegetables, fruits, and herbs that people grow hydroponically. I hope this will help you guys in your hydroponics journey.
Get this reading chart in your inbox.
| Crops | EC (mS/cm) | pH | PPM 500 (USA) | PPM 700 (UK) |
| African Violet | 1.2 to 1.5 | 6.0 to 7.0 | 600 to 750 | 840 to 1050 |
| Ambra Radicchio | 5.5 to 6.5 | |||
| Artichoke | 0.8 to 1.8 | 6.5 to 7.5 | 400 to 900 | 560 to 1260 |
| Asparagus | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6.0 to 6.8 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Banana | 1.8 to 2.2 | 5.5 to 6.5 | 900 to 1100 | 1260 to 1540 |
| Basil | 1.0 to 1.6 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 500 to 800 | 700 to 1120 |
| Bean (Common) | 2.0 to 4.0 | 6 | 1000 to 2000 | 1400 to 2800 |
| Bean (Italian Bush) | 6.0 to 6.5 | |||
| Bean (Lima) | 6.0 to 6.5 | |||
| Bean (Pole) | 6.0 to 6.5 | |||
| Beetroot | 0.8 to 5.0 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 400 to 2500 | 560 to 3500 |
| Bell Peppers | 2.0 to 2.5 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 1000 to 1250 | 1400 to 1750 |
| Black Currant | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Blueberry | 1.8 to 2.0 | 4.0 to 5.0 | 900 to 1000 | 1260 to 1400 |
| Broadbean | 1.8 to 2.2 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 900 to 1100 | 1260 to 1540 |
| Broccoli | 2.8 to 3.5 | 6.0 to 6.8 | 1400 to 1750 | 1960 to 2450 |
| Brussel Sprouts | 2.5 to 3.0 | 6.5 to 7.5 | 1250 to 1500 | 1750 to 2100 |
| Cabbage | 2.5 to 3.0 | 6.5 to 7.0 | 1250 to 1500 | 1750 to 2100 |
| Capsicum | 1.8 to 2.2 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 900 to 1100 | 1260 to 1540 |
| Carnation | 2.0 to 3.5 | 6 | 1000 to 1750 | 1400 to 2450 |
| Carrots | 1.6 to 2.0 | 6.3 | 800 to 1000 | 1120 to 1400 |
| Cauliflower | 0.5 to 2.0 | 6.0 to 7.0 | 250 to 1000 | 350 to 1400 |
| Celery | 1.8 to 2.4 | 6.5 | 900 to 1200 | 1260 to 1680 |
| Chicory | 1.0 to 1.6 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 500 to 800 | 700 to 1120 |
| Chives | 1.8 to 2.4 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 900 to 1200 | 1260 to 1680 |
| Collard Greens | 6.5 to 7.5 | |||
| Courgettes | 1.8 to 2.4 | 6 | 900 to 1200 | 1260 to 1680 |
| Cucumber | 1.7 to 2.0 | 5.0 to 5.5 | 850 to 1000 | 1190 to 1400 |
| Eggplant | 2.5 to 3.5 | 6 | 1250 to 1750 | 1750 to 2450 |
| Endive | 2.5 to 3.5 | 5.5 to 6.5 | 1250 to 1750 | 1750 to 2450 |
| Fennel | 1.0 to 1.4 | 6.4 to 6.8 | 500 to 700 | 700 to 980 |
| Ficus | 1.6 to 2.4 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 800 to 1200 | 1120 to 1680 |
| Fodder | 2.0 to 2.4 | 5.5 | 1000 to 1200 | 1400 to 1680 |
| Garlic | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Hot Peppers | 3.0 to 3.5 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 1500 to 1750 | 2100 to 2450 |
| Lavender | 1.0 to 1.4 | 6.4 to 6.8 | 500 to 700 | 700 to 980 |
| Leek | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6.5 to 7.0 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Leek | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6.5 to 7.0 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Lemon Balm | 1.0 to 1.6 | 5.5 to 6.5 | 500 to 800 | 700 to 1120 |
| Lettuce | 1.2 to 1.8 | 6.0 to 7.0 | 600 to 900 | 840 to 1260 |
| Marjoram | 1.6 to 2.0 | 6 | 800 to 1000 | 1120 to 1400 |
| Marrow | 1.8 to 2.4 | 6 | 900 to 1200 | 1260 to 1680 |
| Melon | 2.0 to 2.5 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 1000 to 1250 | 1400 to 1750 |
| Mint | 2.0 to 2.4 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 1000 to 1200 | 1400 to 1680 |
| Mustard Cress | 1.2 to 2.4 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 600 to 1200 | 840 to 1680 |
| Okra | 1.0 to 2.4 | 6.5 | 500 to 1200 | 700 to 1680 |
| Onions | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6.0 to 6.7 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Pak Choi | 1.5 to 2.0 | 7 | 750 to 1000 | 1050 to 1400 |
| Parsley | 1.8 to 2.2 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 900 to 1100 | 1260 to 1540 |
| Parsnip | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Passionfruit | 1.6 to 2.4 | 6.5 | 800 to 1200 | 1120 to 1680 |
| Paw-Paw | 1.6 to 2.4 | 6.5 | 800 to 1200 | 1120 to 1680 |
| Pea | 0.8 to 1.8 | 6.0 to 7.0 | 400 to 900 | 560 to 1260 |
| Peas (Sugar) | 6.0 to 6.8 | |||
| Pepino | 2.0 to 5.0 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 1000 to 2500 | 1400 to 3500 |
| Peppers | 0.8 to 1.8 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 400 to 900 | 560 to 1260 |
| Pineapple | 2.0 to 2.4 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 1000 to 1200 | 1400 to 1680 |
| Potato | 2.0 to 2.5 | 5.0 to 6.0 | 1000 to 1250 | 1400 to 1750 |
| Pumpkin | 1.8 to 2.4 | 5.5 to 7.5 | 900 to 1200 | 1260 to 1680 |
| Radish | 1.6 to 2.2 | 6.0 to 7.0 | 800 to 1100 | 1120 to 1540 |
| Red Currant | 1.4 to 1.8 | 6 | 700 to 900 | 980 to 1260 |
| Rhubarb | 1.6 to 2.0 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 800 to 1000 | 1120 to 1400 |
| Rose | 1.5 to 2.5 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 750 to 1250 | 1050 to 1750 |
| Rosemary | 1.0 to 1.6 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 500 to 800 | 700 to 1120 |
| Sage | 1.0 to 1.6 | 5.5 to 6.5 | 500 to 800 | 700 to 1120 |
| Silverbeet | 1.8 to 2.3 | 6.0 to 7.0 | 900 to 1150 | 1260 to 1610 |
| Spinach | 1.8 to 2.3 | 6.0 to 7.0 | 900 to 1150 | 1260 to 1610 |
| Squash (Summer) | 5.0 to 6.5 | |||
| Squash (Winter) | 5.0 to 6.5 | |||
| Strawberry | 1.8 to 2.2 | 6 | 900 to 1100 | 1260 to 1540 |
| Sweet Corn | 1.6 to 2.4 | 6 | 800 to 1200 | 1120 to 1680 |
| Sweet Potato | 2.0 to 2.5 | 5.5 to 6.0 | 1000 to 1250 | 1400 to 1750 |
| Swiss Chard | 6.0 to 6.5 | |||
| Taro | 2.5 to 3.0 | 5.0 to 5.5 | 1250 to 1500 | 1750 to 2100 |
| Thyme | 0.8 to 1.6 | 5.5 to 7.0 | 400 to 800 | 560 to 1120 |
| Tomato | 2.0 to 4.0 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 1000 to 2000 | 1400 to 2800 |
| Turnip | 1.8 to 2.4 | 6.0 to 6.5 | 900 to 1200 | 1260 to 1680 |
| Watercress | 0.4 to 1.8 | 6.5 to 6.8 | 200 to 900 | 280 to 1260 |
| Watermelon | 1.5 to 2.4 | 5.8 | 750 to 1200 | 1050 to 1680 |
| Zucchini | 1.8 to 2.4 | 6 | 900 to 1200 | 1260 to 1680 |
FAQ
Do I need an EC meter for hydroponics?
Yes, an EC meter is needed for hydroponic systems. An EC meter helps to determine the concentration of the hydroponic nutrient solution. It also helps in mitigating the risk of bacteria and fungus as you can easily notice the change in the EC of your solution and work to find the root cause.
How to control EC in hydroponics?
To control the EC of your hydroponic nutrient solution, you should know the optimum range of EC levels for the plant you are growing. I have given a comprehensive EC reading chart in this article. If the EC is lower than the optimum reading then add more fertilizer and if the EC is higher than the optimum level, dilute the solution by adding water.
Is EC the same as PPM?
EC is the short form of Electronic Conductivity and PPM is the short form for Parts Per Million. EC meter gives the concentration of the nutrient elements present in the solution. That quantity can be measure in both EC units and PPM. PPM is a common term as it is used to measure the impurity of drinking water at our homes. That is why people prefer to measure EC of nutrient solution also in PPM. 1 EC = EC X 500 for PPM 500 scale (U.S.A.) and 1 EC = EC X 700 for the PPM 700 Scale (U.K.).
Does pH down raise EC?
Yes, reduction in pH level of your nutrient solution can be a reason to increase EC of the solution. As the pH lowers the solution becomes acidic which means the concentration of acidic elemets is increasing and neutral and alkaline elements are being absrobed at a faster rate by the plant.
What should be the EC for hydroponic tomatoes?
The EC for hydroponic tomatoes should be in the range of 2.0 to 4.0. The PPM should be in the range of 1000 to 2000 for PPM 500 scale and 1400 to 2800 in the PPM 700 scale.
Thanks for reading. Let me know in the comments section if you want me to cover any other topic on hydroponics.
Have a Good Day!
How do I calibrate my EC meter?

